One of the most important aspects of composing a photograph is choosing the right lens for the job. Most beginners understand that (from the same distance) telephoto lenses will make their subjects appear larger, and wide angle lenses will make their subjects appear smaller, but there’s a common misconception about how lens choice affects the image as a whole. Many people believe that if you shoot a photo with a 200mm lens, you can recreate the same photo with a 100mm lens by simply getting closer to the subject.
But that’s not quite true.
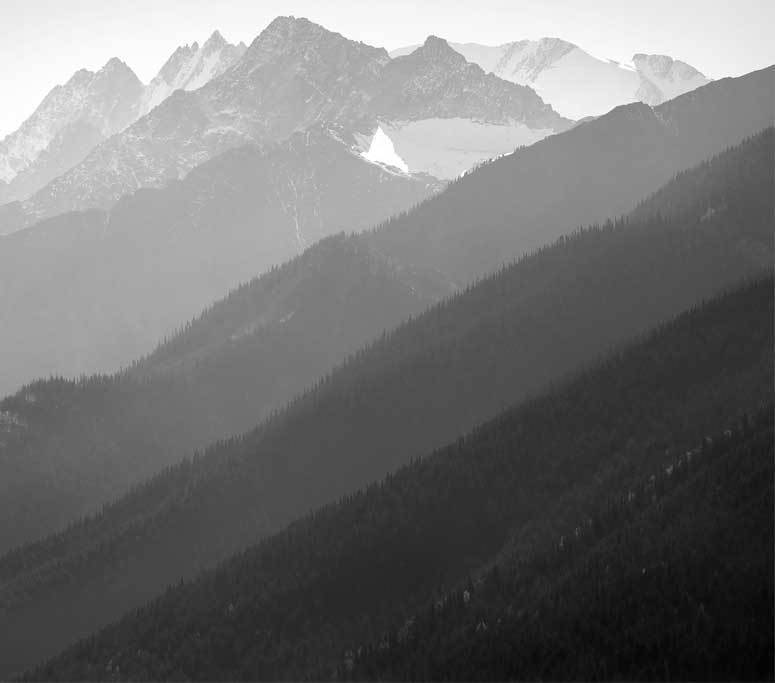
Different lenses don’t just change the size of the elements in your photo, they change the relationship between elements that are closer to the camera and those that are further away. When shooting with wide angle lenses, objects that are close to the camera appear large, but as they get further away, they appear to get smaller very quickly. If, for example, you’re using a wide angle lens to take a full-body shot of a person (with his/her head at the top border of the frame, feet at the bottom border), a person standing 10 feet behind the first one might only appear to be half the size.


.
(I made these weird illustrations with stock photos from dreamstime. Not mine.)
If you used a telephoto lens to take the same photo, though, and composed the shot so that the first person filled the frame the same way, someone standing 10 feet behind them would appear much closer to the same size, and therefore they’d appear to be closer together. In fact, the longer the telephoto lens (eg., a 400mm instead of a 100mm), the closer together they would appear to be. This phenomenon is known as compression.
Telephoto lenses allow you to compress your subject and background together so that they are both large and prominent in the image. Similarly, if you have multiple subjects that are close together horizontally but at different distances (think about a receding view of fence posts/street lights/columns or athletes on a field), those objects can all be brought together in the frame as important compositional elements.
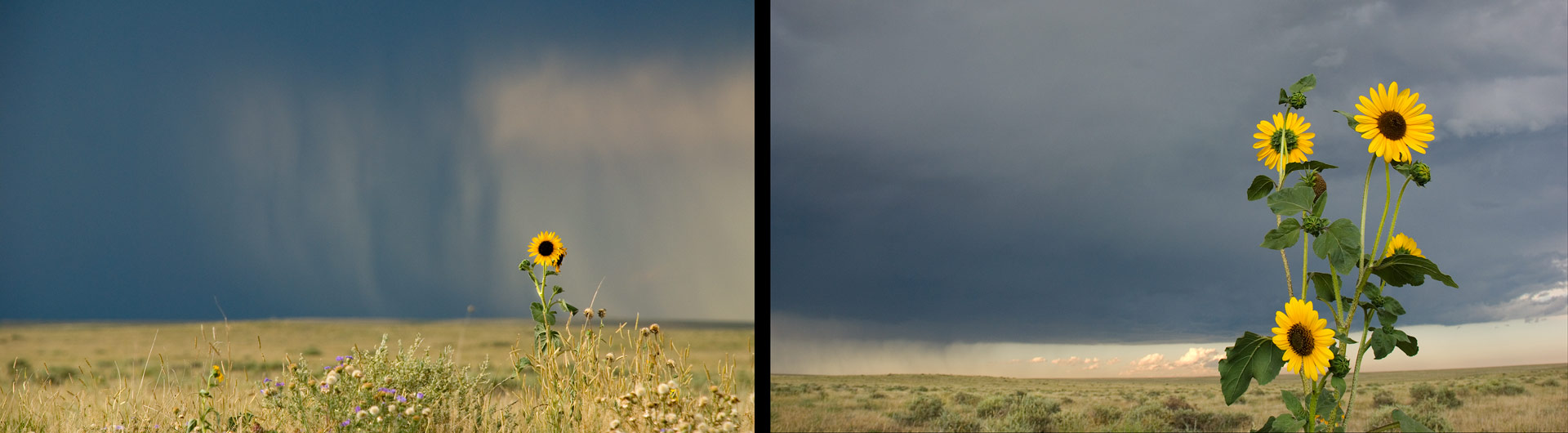

This is especially effective with objects that are very distant but large, like clouds, or the moon. If you photograph the moon with a 600mm lens, it will be a large, prominent part of the photograph. Therefore, if you compose a shot with your subject in the frame and the moon in the background, the moon will appear very large and close to the subject. The potential drawback of shooting this way is that it requires you to be very far away from your subject.
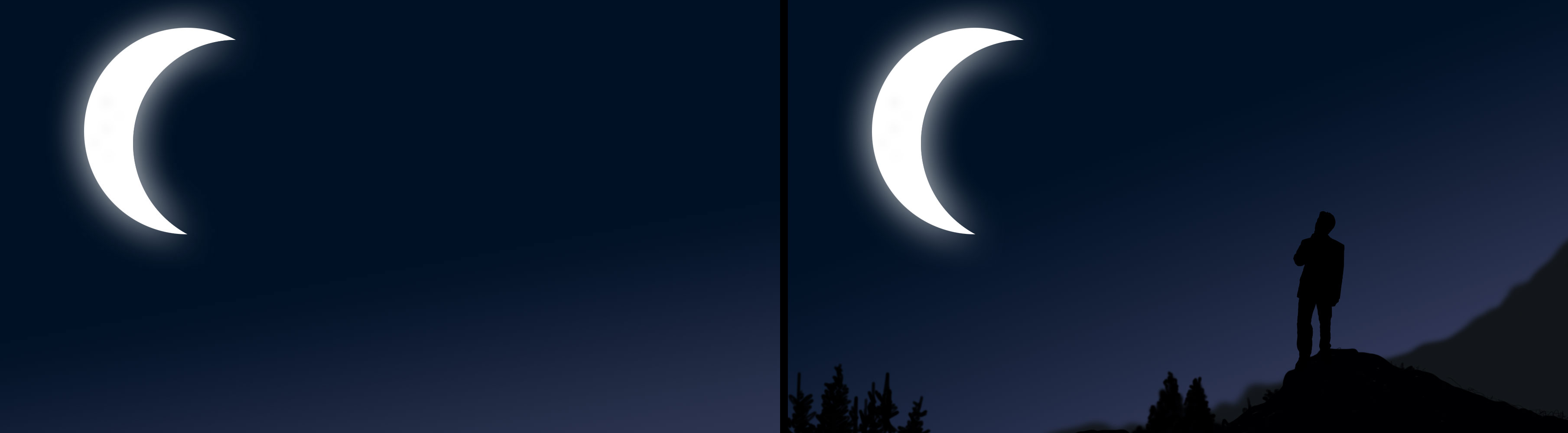

Wide angle lenses, on the other hand, have the opposite effect. Using a wide angle lens allows you to emphasize a subject, making it appear very large in the frame while objects in the background appear very small and distant. Working this way requires you to be very close to your subject, and indeed, it requires the subject to be very close to the background if you want the background to be an important compositional element. Because wide angle lenses increase the apparent distance between objects in the frame, they’re very useful for highlighting a diminishing perspective in an image.
In the video example above, I shot a series of photos of a rowboat with wide and telephoto lenses. I started with a telephoto lens, and stood perhaps 100 feet away from the boat. As I zoomed out, I walked towards it to keep the boat the same size in the frame. In the final shot, I was no more than 2 meters away from the boat, using an 18mm lens (at which point the barrel distortion was so great that I was no longer able to correct it completely in post processing). The progression shows how choosing a different lens and shooting from a different location can dramatically affect your overall image.
What Causes Compression?
Compression is not really caused by the lens so much as it is caused by the fact that different lenses require photographers to move further or closer to their subjects to frame them similarly, and this change in distance changes the relationships between the photographer and the objects being photographed.
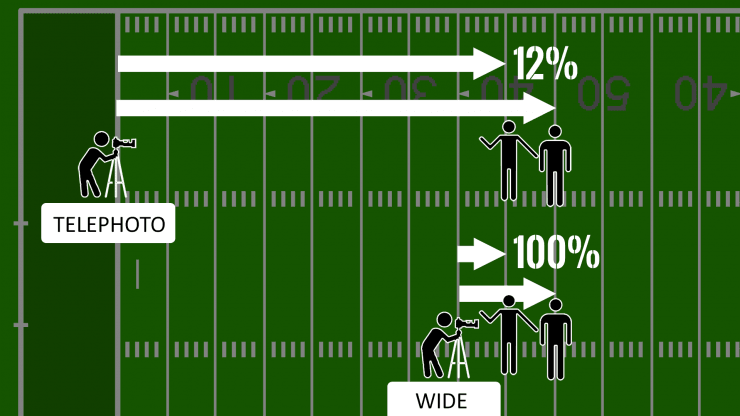
For example: suppose you’re photographing two people who are standing on a football field, one is closer to you and standing on the 40 yard line, and the other is further away, standing on the 45 yard line. If you photograph them from the end-zone with a long telephoto lens to make the closer player fill the frame, the second player will also be about the same size because he’s not much further away compared to the first player.
If, on the other hand, you use a wide angle lens to frame the first player the same way, you’d need to move way out to the 35 yard line yourself. From there, the second player is twice as far away from you as the first player, so the lens choice has changed the relationship between the two players from being 11% to 50% different in distance from you.
Finally, it’s important to mention that the focal length of the lens has a dramatic impact on how out-of-focus the background of the image appears. All of the photos in the video example above were shot at the same aperture, but the background looks pretty blurry in the telephoto shots, but relatively sharp as it gets closer to wide angle. The reason for this is simple: the objects in the background are much smaller in the wide angle shots, so even though they’re just as blurry as they are in the telephoto shots, it’s very hard to see the blur (for the same reason, small prints look sharper than large ones). Conversely, when you use a telephoto lens, the blurred background is magnified, giving you a much smoother, more distinct blurring effect which is suitable for portraits.
Examples?
Again, rather than filling this gallery with my own images, I’d like to see some of yours! They don’t need to be artistically or technically perfect… simply email me your photo (any size) that is a clear example of how your lens choice played an important part in the composition, and I’ll add it to a gallery. Members can also attach them to comments below. Please also include how you’d like your name to appear in the byline, either as your username here, or your real name.




